Understanding the Immune System’s Need for Support
The human immune system is a complex and dynamic network that defends the body against harmful pathogens, environmental toxins, and internal threats such as abnormal cell growth. This vital system is influenced by a multitude of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, stress levels, sleep patterns, and nutritional status. In recent years, growing attention has been placed on the intricate relationship between gut health and immune function. This is where the conversation about probiotics for immunity begins to take center stage. These living microorganisms, often referred to as “good bacteria,” have shown promising benefits in strengthening immune defenses and maintaining the delicate balance of the gut microbiota.
Probiotics are most commonly associated with digestive health, but their influence extends well beyond the gut. Research now supports their role in modulating immune responses, reducing the incidence of infections, and enhancing the effectiveness of certain vaccines. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), which comprises a significant portion of the immune system, thrives in the presence of a healthy and diverse gut microbiome. Thus, it becomes increasingly evident that probiotics for immunity are not just a wellness trend but a scientifically backed approach to supporting long-term health.
When individuals seek ways to naturally boost their immune system, questions often arise: do probiotics help the immune system? Are all probiotic strains equally effective? What makes certain formulations more beneficial than others? These questions underscore the need for a deeper understanding of how to select high-quality probiotic supplements tailored to immune support. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the mechanisms behind probiotics and immune function, the specific strains that contribute to immunity, and practical advice on choosing products that are not only evidence-based but also aligned with individual health needs.
You may also like: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing an Effective Immune Support Supplement for Daily Wellness
How Probiotics Influence Immune Function
To appreciate the role of probiotics in immune support, one must first understand how they interact with the body’s existing immune pathways. Probiotics exert their effects through several interconnected mechanisms. They strengthen the epithelial barrier of the intestinal lining, preventing the entry of harmful pathogens into the bloodstream. This physical barrier is reinforced by the production of antimicrobial substances such as bacteriocins and lactic acid, which inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and maintain the balance of the microbiota.
Moreover, probiotics have the ability to modulate the immune system by influencing both innate and adaptive immunity. They stimulate the activity of macrophages, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells, which are crucial components of the first line of immune defense. These interactions help the body respond more efficiently to infections and reduce the risk of systemic inflammation. On the adaptive side, probiotics promote the production of regulatory T cells and immunoglobulins such as IgA, which help fine-tune immune responses and maintain tolerance to non-threatening stimuli.
An equally important aspect of probiotics for immune function is their role in controlling inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of many autoimmune and metabolic disorders, and certain probiotic strains have demonstrated the ability to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and interleukin-6. This anti-inflammatory effect is particularly relevant in conditions where immune overactivation contributes to disease progression, including allergies and inflammatory bowel diseases.
By supporting mucosal immunity, enhancing barrier function, and regulating immune signaling, probiotics serve as essential allies in promoting a balanced immune response. The effectiveness of these functions, however, is highly strain-specific. This means that not all probiotics confer the same benefits, and understanding which strains offer the most value for immune health is critical when selecting a supplement.
Top Strains of Probiotics for Immunity
Among the myriad of probiotic strains available on the market, only a select few have been studied extensively for their immune-supporting properties. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genera are among the most well-documented and widely used in clinical research. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, for example, has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of respiratory infections in both children and adults. Its ability to enhance the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and support gut integrity makes it a popular choice in immune-focused formulations.
Another standout strain is Bifidobacterium lactis HN019, known for its immunomodulatory properties and its role in enhancing the activity of natural killer cells. Clinical trials have indicated that regular supplementation with B. lactis HN019 can improve immune markers in elderly populations, who are particularly vulnerable to immune decline. Similarly, Lactobacillus casei Shirota has been linked to improvements in vaccine response and a reduction in the frequency of upper respiratory tract infections.
Lactobacillus plantarum is another powerhouse strain that supports the gut barrier and reduces systemic inflammation. Its presence in fermented foods like sauerkraut underscores the traditional understanding of fermented foods as health-promoting staples. Additionally, Bifidobacterium longum is known for its ability to alleviate gastrointestinal inflammation and support mental health through the gut-brain axis, which in turn indirectly influences immune function.
Understanding the role of each strain is essential, as different probiotics for immune support target distinct pathways and populations. A child with frequent colds may benefit from a different formulation than an adult managing chronic inflammation. Therefore, seeking out specific strains with clinical evidence for the intended use is a fundamental step in making an informed supplement choice.
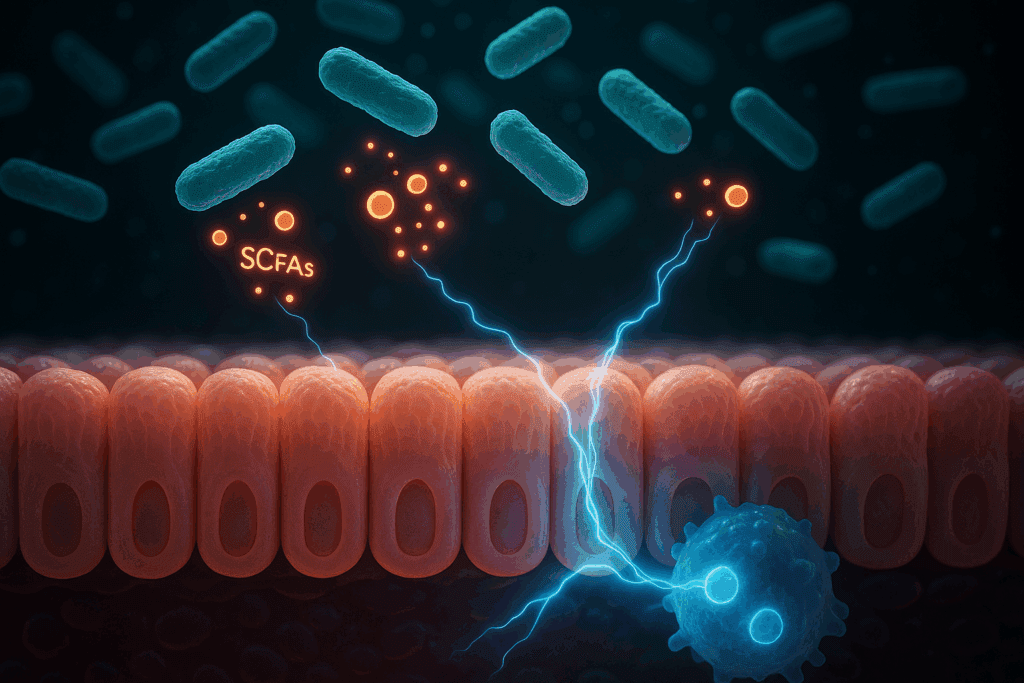
The Science Behind Probiotics for Immune Support
Scientific validation is a cornerstone of any health intervention, and probiotics are no exception. Over the past two decades, a growing body of randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses has examined the efficacy of probiotics for immune system enhancement. Studies have demonstrated that probiotics can reduce the incidence, duration, and severity of common infectious diseases, including the common cold, influenza, and gastrointestinal infections. These effects are particularly notable in children, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
One meta-analysis published in the journal Nutrients found that probiotic supplementation significantly reduced the number of acute respiratory infections and days absent from work or school. Another study, featured in Clinical Nutrition, concluded that probiotic use resulted in a substantial decrease in the need for antibiotic prescriptions, highlighting their role in preventative care. These findings affirm that do probiotics help immune system function? The answer is increasingly clear: yes, especially when targeted strains are used consistently.
Mechanistically, these benefits are attributed to the ability of probiotics to modulate gene expression, influence metabolic signaling, and enhance the resilience of the gut microbiome. Emerging research in the field of metabolomics reveals that probiotic bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, which not only nourish colonocytes but also play a role in systemic immune regulation. SCFAs contribute to the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis and help prevent leaky gut, a condition associated with immune dysfunction and systemic inflammation.
Additionally, clinical studies have highlighted the potential of probiotics in improving vaccine efficacy. By enhancing the body’s immune responsiveness, probiotics can amplify antibody production following immunization. This is particularly relevant in populations with weakened immunity, such as the elderly or individuals with chronic health conditions. Thus, the clinical evidence supporting probiotics for immune function continues to grow, reinforcing their place in a comprehensive health strategy.

Probiotics for Immunity: What to Look for in a Supplement
Choosing a probiotic supplement can be overwhelming given the sheer number of products available, each boasting different strains, dosages, and delivery systems. To identify the most effective probiotics for immunity, consumers should prioritize several key factors. First and foremost is the presence of well-studied strains with documented benefits for immune support. This includes those mentioned earlier, such as L. rhamnosus GG, B. lactis HN019, and L. plantarum. Products should clearly label the strain designation (e.g., Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG rather than just Lactobacillus rhamnosus) to ensure traceability and scientific credibility.
Dosage is another critical consideration. The efficacy of a probiotic often depends on achieving a threshold number of colony-forming units (CFUs). While this can vary by strain and condition, a general recommendation for immune health is between 1 billion and 10 billion CFUs per day. However, higher doses do not always translate to greater benefits. The context of use, such as age, immune status, and health goals, should guide dosage decisions.
Equally important is the method of delivery. Probiotics are sensitive to heat, moisture, and gastric acidity, which can destroy viable bacteria before they reach the intestine. Look for formulations with protective technologies such as enteric coatings or delayed-release capsules that safeguard against stomach acid. Some products also incorporate prebiotics—non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial bacteria—to enhance probiotic survival and colonization.
Quality assurance practices such as third-party testing, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) certification, and transparency in labeling also contribute to a product’s reliability. Reputable brands will provide detailed information about storage conditions, expiration dates, and clinical studies supporting their formulations. By prioritizing these features, individuals can more confidently select probiotics for immune support that are both safe and effective.
Real-World Applications of Probiotics for Immunity
Incorporating probiotics into daily life extends beyond supplementation alone. While capsules and powders offer concentrated doses, many fermented foods naturally contain probiotic strains that support immune health. Yogurt with live cultures, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and kombucha are rich sources of beneficial bacteria and have been consumed for centuries for their health-promoting properties. These foods provide a synergistic combination of probiotics and bioactive compounds that reinforce gut health and immune resilience.
For individuals managing chronic illnesses or undergoing treatments that suppress immunity, probiotics may offer a protective buffer. Cancer patients receiving chemotherapy, for instance, often experience disruptions in gut flora that increase susceptibility to infections. Clinical evidence suggests that probiotics can help restore microbial balance and reduce gastrointestinal side effects, though medical supervision is essential in such cases.
In pediatric settings, probiotics have shown potential in preventing eczema, reducing the severity of colic, and lowering the incidence of respiratory tract infections. For older adults, who may face immunosenescence—a gradual decline in immune function—probiotics offer a natural avenue to bolster defense mechanisms. Athletes, too, benefit from probiotic use by mitigating exercise-induced immune suppression, which can leave them vulnerable to illness post-training.
These real-world examples underscore the versatility of probiotics for immune system support across different life stages and health contexts. They also highlight the importance of integrating probiotics into a broader lifestyle approach that includes balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep—all essential pillars of immune health.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Probiotics for Immunity
Despite the growing popularity of probiotics, misconceptions continue to circulate. One common myth is that all probiotic products are equally effective. In reality, the health benefits of probiotics are highly strain-specific, and not all formulations are backed by scientific evidence. Taking a random probiotic without understanding its strain or intended use may yield little to no benefit.
Another misconception is that probiotics are a cure-all solution for immune dysfunction. While they can play a supportive role, they are not substitutes for a healthy lifestyle, medical treatments, or vaccines. The effectiveness of probiotics is influenced by factors such as dosage, consistency of use, and the individual’s baseline health status. Overreliance on probiotics without addressing other lifestyle factors may limit their potential impact.
Some people also believe that more CFUs automatically mean a better product. However, excessively high doses may not provide added benefits and could even cause digestive discomfort in some individuals. The key is not the highest number but the right strains at the appropriate dosage for the desired effect.
Finally, there is a misconception that refrigerated probiotics are always superior. While refrigeration can enhance shelf life, many high-quality products use freeze-drying and protective coatings to maintain viability at room temperature. This makes them more convenient without compromising effectiveness. Consumers should focus on stability and strain specificity rather than storage conditions alone.
By dispelling these myths and educating consumers on the nuances of probiotic supplementation, we empower individuals to make more informed and effective choices for immune health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Probiotics for Immunity
How do environmental factors influence the effectiveness of probiotics for immunity?
Environmental exposures—such as air pollution, heavy metals, and even water contaminants—can negatively impact the gut microbiota and, consequently, immune function. Probiotics for immunity can help counteract some of these effects by reinforcing the gut barrier and restoring microbial balance, but their success may vary depending on an individual’s exposure levels. For example, individuals living in urban environments may benefit from probiotic strains known to reduce oxidative stress, like Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3. Seasonal changes, particularly during flu season or allergy peaks, may also influence how probiotics for immune support function, necessitating temporary changes in strain selection or dosage. Adjusting probiotic regimens based on environmental stressors is a strategy that can further enhance their effectiveness in immune modulation.
Can combining probiotics with other supplements enhance immune function?
Yes, pairing probiotics for immune function with other targeted supplements can result in synergistic effects. For instance, combining probiotics with vitamin D may amplify mucosal immune responses, as both are involved in maintaining epithelial integrity and immune signaling. Zinc is another micronutrient that supports the development of immune cells, and when taken alongside probiotics, it may improve resistance to respiratory infections. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids can reduce systemic inflammation, working in tandem with anti-inflammatory probiotic strains like Bifidobacterium breve. However, combining supplements should be done thoughtfully to avoid interactions and to ensure each component is backed by research for its role in immune support.
Do probiotics help immune system recovery after antibiotic use?
Antibiotic therapy often leads to collateral damage in the gut microbiota, depleting beneficial bacterial populations that are integral to immune function. Probiotics can aid in restoring microbial diversity, thereby accelerating immune recovery post-antibiotic treatment. Certain strains like Saccharomyces boulardii and Lactobacillus reuteri have been shown to reduce antibiotic-associated diarrhea and rebalance intestinal flora. Integrating probiotics for immune system support during and after antibiotic regimens may reduce the risk of secondary infections and support long-term gut health. However, timing is important—probiotics should be taken a few hours apart from antibiotics to ensure maximum survival and colonization.
What are some emerging trends in probiotics for immune support?
One of the most exciting trends in probiotics for immune support involves the rise of next-generation probiotics, including strains like Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. These microbes, though not traditionally available in supplements, are being researched for their powerful anti-inflammatory and mucosal-protective effects. Another trend is the integration of precision probiotics, which tailor formulations based on an individual’s microbiome profile through DNA sequencing. Additionally, spore-based probiotics are gaining popularity due to their resilience and ability to survive harsh conditions within the digestive tract. These innovations represent the future of personalized and effective probiotic interventions for immune function.
Can probiotics influence vaccine effectiveness?
Emerging research suggests that probiotics may enhance vaccine efficacy by modulating mucosal immunity and increasing antigen-specific antibody responses. Clinical trials have demonstrated improved outcomes with vaccines for influenza, rotavirus, and even HPV when participants also received certain probiotic strains like Lactobacillus paracasei or Bifidobacterium lactis. These probiotics for immune support may prime the immune system to respond more robustly by improving antigen presentation and stimulating dendritic cell activity. This potential application is particularly relevant for immunocompromised individuals or the elderly, whose vaccine responses may be diminished. Future studies are likely to focus on strain-specific combinations that can act as safe adjuvants for improving immunization outcomes.
What lifestyle factors amplify the benefits of probiotics for immunity?
While taking probiotics is beneficial, their effectiveness is magnified when combined with healthy lifestyle habits. Regular physical activity has been shown to increase microbial diversity and improve the colonization of beneficial strains. Sleep hygiene is another critical factor; inadequate sleep can disrupt the circadian rhythm of the microbiome, reducing the effectiveness of probiotics for immune function. Managing stress through mindfulness or cognitive behavioral techniques also supports gut health, as chronic stress can increase intestinal permeability and inflammation. A fiber-rich, plant-based diet acts as a natural prebiotic, feeding probiotic bacteria and enhancing their survival and function. These lifestyle factors form a holistic foundation that complements the use of probiotics for immune system health.
How do age and life stage affect the need for probiotics for immunity?
The need for probiotics for immune function varies across the lifespan. Infants benefit from strains like Bifidobacterium infantis, which aid in developing a robust immune system during early colonization. Children, especially those in daycare or school settings, often experience recurrent infections, and strains such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG can reduce their frequency. In adults, stress, diet, and antibiotic use are major disruptors of gut health, making probiotics a valuable tool for maintaining immune resilience. Older adults experience immunosenescence, a natural decline in immune function, which can be countered with strains like Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 to enhance natural killer cell activity. Each life stage presents unique immune challenges that targeted probiotics can address effectively.
Are probiotics for immunity safe for individuals with autoimmune conditions?
The safety and efficacy of probiotics for immune system support in autoimmune populations are increasingly being studied, with promising but cautious optimism. Certain probiotic strains, particularly those with anti-inflammatory properties, may help modulate immune overactivity without triggering flare-ups. For instance, Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus plantarum have been examined for their roles in reducing inflammatory cytokines in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis. However, the strain-specific nature of probiotics means that not all options are suitable for all autoimmune conditions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor probiotic use to the individual’s medical history, disease activity, and concurrent treatments.
How can travelers use probiotics to support immunity on the go?
Travel exposes individuals to unfamiliar pathogens, stress, disrupted sleep, and dietary changes—all of which can compromise the immune system. Probiotics for immunity are especially helpful during travel to reduce the risk of traveler’s diarrhea and other gastrointestinal illnesses. Shelf-stable strains like Bacillus coagulans and Saccharomyces boulardii are ideal for travel due to their resilience in varying temperatures and pH levels. Probiotic supplementation prior to, during, and after travel helps maintain a balanced gut microbiome and supports immune vigilance during exposure to new environments. Many seasoned travelers incorporate probiotics into their pre-trip health routine as a proactive wellness measure.
Why does probiotic strain diversity matter for immune health?
Diversity among probiotic strains ensures a broader range of immune benefits, as different strains target different mechanisms. Some strains are more effective at reinforcing the gut barrier, while others enhance systemic immunity or reduce inflammation. Using a multi-strain probiotic may provide a more comprehensive approach to immune support by covering multiple pathways simultaneously. For example, combining Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Streptococcus thermophilus may yield synergistic effects in maintaining mucosal immunity. This diversity mimics the natural variety found in a healthy gut microbiota, making probiotic formulations more effective for long-term immune system balance. Ensuring a varied intake—whether through supplements or fermented foods—can be a powerful strategy for enhancing probiotics for immune support.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices for Long-Term Immune Wellness
As the body of evidence continues to grow, it becomes increasingly clear that probiotics for immunity represent a scientifically grounded and practical approach to enhancing overall health. These living microorganisms influence immune responses through a variety of mechanisms, including strengthening gut integrity, regulating inflammation, and promoting the activity of immune cells. The synergy between gut health and immune resilience reinforces the importance of nurturing a balanced and diverse microbiome.
For those considering probiotics as part of their immune support regimen, the journey begins with informed selection. Not all products are created equal, and identifying specific strains with clinical validation is essential. Understanding the role of dosage, delivery mechanisms, and quality standards can help ensure that the chosen supplement delivers real, measurable benefits. Whether through high-quality supplements or probiotic-rich foods, consistent intake is key to maintaining a healthy gut-immune connection.
Additionally, integrating probiotics into a holistic wellness strategy that includes nutrient-rich foods, physical activity, stress reduction, and adequate sleep will provide the most robust support for immune function. While the question of do probiotics help immune system health has largely been answered by current research, the continued exploration of new strains and applications promises even greater benefits in the years to come.
Ultimately, the goal is not just to prevent illness but to cultivate a resilient, well-regulated immune system that supports vitality at every stage of life. With the right knowledge and tools, probiotics for immune support can become a cornerstone of a smarter, more proactive approach to daily wellness.
Further Reading:
How to Choose the Best Probiotic Supplement—This Is What They Said