Introduction
In the evolving landscape of nutrition science, the search for foods that not only fuel the body but also actively support weight loss, cognitive performance, and metabolic efficiency has grown stronger. One standout in this arena is MCT oil and the family of MCT-rich foods that offer a unique advantage for those aiming to burn fat, stay energized, and even improve brain function. MCT, or medium-chain triglycerides, are a specific type of saturated fat that behaves quite differently from the long-chain fats found in most diets. Instead of being stored in fat tissue, MCTs are rapidly absorbed, sent directly to the liver, and metabolized for energy or ketone production.
You may also like: MCT Oil for Dementia and Brain Health: Exploring Its Role in Memory, Function, and Alzheimer’s Support
The rise of the MCT oil ketogenic diet has popularized these functional fats, but many people are still unsure about how much to consume, which foods contain them, and how they fit into a sustainable wellness plan. There’s also growing interest in the cognitive potential of MCTs, especially for those managing conditions like ADHD. In fact, many women are asking, how many mg of MCT for female adult ADHD is optimal, or how many mg of MCT oil for female adult ADHD will boost focus without side effects?
This article offers a deep dive into the MCT diet and answers the most essential questions surrounding MCT foods for weight loss and metabolic health. We’ll explore the top foods high in MCTs, the MCT foods list you can shop from, practical insights into how to use MCT oil daily, and even whether organic MCT oil is better than non-organic. We’ll also clarify myths, explain the benefits of MCT oil in coffee, and uncover exactly what does MCT oil do for keto success. Whether you’re optimizing body composition, exploring MCT oil benefits for cognition, or simply curious about what foods are high in MCT, this comprehensive guide has you covered.
What Are MCTs and Why Do They Matter?
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are a subset of saturated fats composed of medium-length carbon chains—specifically between 6 and 12 carbon atoms. This structure makes them metabolically unique. Unlike long-chain triglycerides (LCTs), MCTs bypass the traditional digestive route. They’re absorbed through the portal vein and delivered directly to the liver, where they’re swiftly converted into energy or ketones. These ketones can fuel both muscles and the brain, making MCTs a valuable energy source for those on a low-carb or ketogenic diet.
The primary MCTs include caproic acid (C6), caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), and lauric acid (C12). While lauric acid is technically on the longer end and behaves more like an LCT in some studies, it still offers benefits when sourced from foods rich in MCTs such as coconut oil. Caprylic and capric acids are considered the most potent for rapid ketone generation and metabolic boost.
Given these properties, it’s no surprise that MCT oil benefits extend beyond energy. They include enhanced fat oxidation, appetite suppression, improved cognitive performance, and potential therapeutic applications for neurological conditions such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and ADHD. This fat-burning profile is also the core reason why MCT foods for weight loss are becoming a staple in fat-loss and metabolic health protocols worldwide.
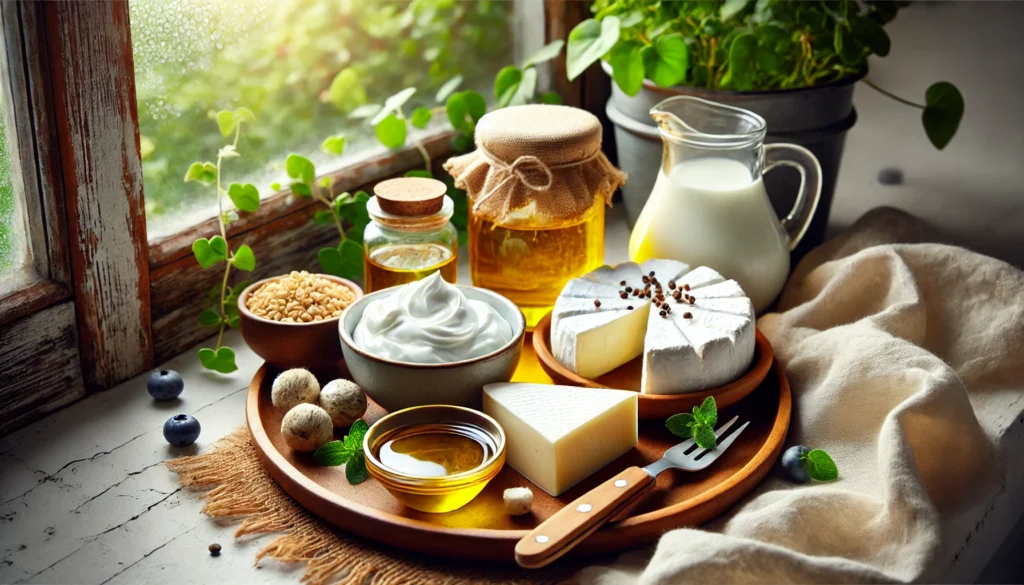

What Foods Have MCTs? Understanding the MCT Foods List
Understanding what foods have MCT naturally helps broaden dietary variety without relying solely on supplements. While MCT oil is the most concentrated source, nature offers a surprising range of foods with MCTs that can complement a clean, energy-focused diet.
Coconut oil is by far the most well-known source of natural MCTs, containing about 54% MCTs by fat content. It includes a mixture of caprylic, capric, and lauric acids. Palm kernel oil is another MCT-rich food, though sustainability concerns make coconut oil the preferred option for environmentally conscious consumers. Dairy products from grass-fed animals—including full-fat yogurt, butter, ghee, and heavy cream—also contain small but meaningful amounts of MCTs, particularly in the form of capric and caprylic acid.
For those seeking plant-based alternatives, some nuts and seeds contain trace amounts of MCTs, though not in therapeutic levels. While fruits high in MCT are virtually nonexistent (fruits are naturally low in fat), tropical fruits consumed with MCT-containing fats can enhance their satiety and glycemic effects.
If you’re building a foods with MCTs list, include the following foundational items: virgin coconut oil, MCT oil, grass-fed butter, goat cheese, organic ghee, palm kernel oil (if sustainably sourced), and full-fat dairy from pasture-raised animals. Each of these supports MCT intake while also contributing to a wholesome, nutrient-dense dietary framework.

The Best MCT Foods for Weight Loss: Metabolic Impact and Usage
When evaluating what are the best MCT foods for weight loss, several criteria come into play: MCT concentration, bioavailability, digestion rate, and complementary macronutrients. For example, pure MCT oil is unmatched in its concentration and rapid conversion to ketones, making it an ideal option for those seeking fasted-state energy or appetite suppression during intermittent fasting.
Coconut oil ranks next in practicality, as it’s more affordable and widely available than refined MCT oil while still offering a significant MCT profile. Though it’s less potent, coconut oil adds texture and flavor to meals, making it easier to use in cooking. Adding MCT oil to coffee in the morning—a practice often referred to as “keto coffee” or “bulletproof coffee”—is a popular method for amplifying thermogenesis and promoting satiety early in the day.
Grass-fed butter and ghee, although lower in MCT concentration, contain fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, which work synergistically with MCTs to enhance metabolic and cognitive function. These are ideal in higher-fat keto meals or as part of a MCT superfoods list that supports hormonal health and long-term satiety.
Combining these foods with high-protein, low-carbohydrate vegetables and quality proteins amplifies the fat-burning potential of a MCT diet. When used thoughtfully, MCT foods for weight loss can elevate metabolic flexibility and make it easier to shift into a fat-burning state without feeling deprived.
How Much MCT Oil Per Day Is Safe and Effective?
Determining how much MCT oil per day is right for you depends on your goals, digestive tolerance, and dietary context. For most people, the recommended dosage begins at 1 teaspoon daily, gradually increasing to 1 to 2 tablespoons. This titration helps avoid common side effects such as gastrointestinal distress, which can occur when starting too aggressively.
For therapeutic purposes—such as cognitive enhancement or support for conditions like epilepsy or ADHD—dosages may reach up to 30 grams per day, split across multiple meals. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before engaging in high-dosage MCT protocols, especially if you have underlying metabolic or digestive conditions.
If your aim is fat loss or appetite control, 1 to 2 teaspoons before meals or during fasting windows may suffice. Meanwhile, athletes seeking performance benefits often consume MCT oil pre-workout to support endurance and mental clarity.
Notably, adding MCT oil to coffee remains one of the most efficient methods for leveraging its fat-burning benefits without complicating your diet. Still, moderation is key, and how to use MCT oil should always be tailored to your specific physiology and lifestyle.
What Does MCT Oil Do for Keto? Unlocking Ketogenic Potential
In the context of a MCT oil ketogenic diet, MCT oil offers several advantages. First, it provides a rapid source of fuel that supports the liver’s production of ketones. For those new to keto or transitioning from a high-carb lifestyle, MCT oil helps bridge the energy gap and minimize symptoms of the “keto flu,” which can occur as the body adapts to using fat instead of glucose for energy.
Second, MCT oil allows for more dietary flexibility. Because it elevates ketone levels even in the presence of small amounts of carbohydrates, it can support “keto cycling” or more lenient forms of low-carb dieting. This is particularly useful for those who want to maintain some carb intake for hormonal balance or athletic performance while still accessing fat-burning benefits.
Third, MCT oil may enhance mental clarity, mood, and brain performance. Ketones are neuroprotective and provide a clean-burning energy source for the brain. This is especially relevant for people using MCT oil to address cognitive issues or to boost productivity and focus during demanding tasks.
In short, what does MCT oil do for keto? It accelerates adaptation, sustains energy, reduces appetite, and improves brain function—making it a cornerstone of many successful ketogenic nutrition strategies.
MCT Oil and ADHD: Dosage, Brain Benefits, and Emerging Science
Interest is growing around the use of MCT oil for cognitive enhancement and neurological support, especially in ADHD populations. Women in particular are asking, how many mg of MCT oil for female adult ADHD is effective without being overstimulating or disruptive.
While definitive clinical dosing guidelines have not yet been universally established, emerging studies suggest that 10 to 15 grams per day—divided into smaller doses—may support attention, executive function, and mood regulation. MCTs, particularly caprylic acid (C8), enhance ketone availability and provide immediate fuel for brain cells. This rapid delivery system may help stabilize energy in the prefrontal cortex, where attention and focus are regulated.
Importantly, how many mg of MCT for female adult ADHD may differ from male or pediatric populations due to hormonal and metabolic differences. Therefore, it’s advisable to start with a small dose (e.g., 1 gram or less) and monitor cognitive response, energy, and gastrointestinal tolerance before adjusting upward.
Using MCT oil alongside nutrient-dense MCT-rich foods such as pasture-raised butter, eggs, and coconut-based products can create a brain-supportive nutritional environment. These dietary habits may enhance neurotransmitter balance and overall mental performance over time.
Organic vs. Non-Organic MCT Oil: Is There a Difference?
Many consumers wonder, is organic MCT oil better than non-organic MCT oil? The distinction primarily revolves around sourcing and purity. Organic MCT oil is typically extracted from coconuts grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, and the processing is usually free of harmful solvents or additives. For people concerned about environmental toxins, sustainability, or chemical exposure, organic MCT oil is the preferred choice.
Non-organic MCT oil may still offer the same core medium-chain fatty acids (caprylic and capric acids), but the sourcing and processing can vary in quality. It may be derived from palm kernel oil, which carries ecological implications, and it may undergo chemical extraction methods that reduce overall purity.
Ultimately, if you’re committed to clean eating and minimizing toxic load, opting for organic is a smart move. While the MCT oil benefits remain present in both types, organic products often reflect better sourcing transparency, which aligns with the values of many health-conscious consumers.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the top natural foods high in MCTs?
Natural foods high in MCTs include virgin coconut oil, palm kernel oil, grass-fed butter, organic ghee, and full-fat goat dairy products. These foods contain various levels of caprylic, capric, and lauric acids—the core MCTs known for rapid absorption and fat-burning benefits. Although fruits and vegetables contain little to no MCTs, combining them with MCT-rich fats can improve nutrient uptake and satiety. For practical daily use, coconut oil remains the most accessible whole-food source of MCTs in most households.
2. How do MCT foods support weight loss?
MCT foods for weight loss work by enhancing thermogenesis, increasing satiety, and encouraging the body to burn fat for fuel. Unlike long-chain fats, MCTs are not stored easily in adipose tissue; instead, they’re rapidly oxidized in the liver. This fast energy conversion reduces hunger hormones, supports stable blood sugar, and may lead to fewer cravings. Over time, incorporating MCT-rich foods into a balanced diet can contribute to a mild caloric deficit and improved metabolic efficiency—both of which support sustainable fat loss.
3. How much MCT oil should I take per day?
For beginners, how much MCT oil per day should start at 1 teaspoon and gradually increase to 1–2 tablespoons as tolerated. Taking too much too quickly may cause digestive upset. For cognitive support or athletic performance, dosages up to 30 grams per day can be split across meals. Always consult your healthcare provider if you’re using MCT oil therapeutically or alongside medication. Personal goals—such as weight loss, energy, or mental clarity—should guide your final dosage plan.
4. Can I get enough MCTs from food without using oil?
Yes, you can obtain moderate levels of MCTs from MCT-rich foods, especially if your diet includes daily servings of coconut oil, grass-fed butter, and full-fat goat dairy. However, if you’re seeking high levels of ketone production or using MCTs therapeutically for ADHD, epilepsy, or cognitive performance, MCT oil provides a more concentrated and efficient delivery. Whole-food MCT sources are ideal for foundational support, while the oil is best for targeted applications.
5. Are there fruits high in MCT?
Despite frequent searches for fruits high in MCT, the reality is that fruits are naturally low in fat and contain virtually no MCTs. However, tropical fruits like avocado or coconut flesh—technically a fruit—can be part of MCT-supportive diets. When paired with fats like coconut oil or ghee, even low-fat fruits can be metabolically balanced. For anyone on a keto or low-carb plan, it’s better to prioritize MCT-rich fats and use fruits for micronutrient variety.
6. Is there a list of MCT superfoods to follow?
Yes, a MCT superfoods list would include: virgin coconut oil, MCT oil, grass-fed butter, organic ghee, full-fat goat yogurt, pasture-raised eggs, and fatty goat cheese. These foods not only supply MCTs but also deliver fat-soluble vitamins and bioavailable minerals that support digestion, brain health, and hormonal balance. Incorporating these daily helps maintain metabolic flexibility, appetite control, and energy regulation in a whole-food context.
7. Does MCT oil have omega-3s?
No, MCT oil does not have omega-3 fatty acids. MCTs are a type of saturated fat, while omega-3s are polyunsaturated fats typically found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and walnuts. However, MCT oil can be combined with omega-3 sources to create a well-rounded lipid profile. This synergy supports inflammation reduction, brain health, and cardiovascular function. For comprehensive fat intake, it’s ideal to include both MCTs and omega-3s in your daily nutrition.
8. How should I use MCT oil in coffee?
The benefits of MCT oil in coffee include enhanced mental clarity, appetite suppression, and ketone production—especially during intermittent fasting. To use it properly, blend 1 teaspoon to 1 tablespoon of MCT oil into hot black coffee, optionally with grass-fed butter or ghee for a richer texture. Avoid stirring, as it won’t emulsify properly. This practice supports metabolic energy and focus for several hours and can help reduce the need for early-morning snacking.
9. What are the best foods with high MCT content?
The best foods with high MCT content are MCT oil (100% MCTs), virgin coconut oil (approximately 54% MCTs), palm kernel oil, grass-fed butter, and goat milk products. These deliver concentrated caprylic and capric acids that support fast energy and fat-burning. Among solid foods, coconut-based items and dairy from grass-fed animals offer the highest MCT concentration. Including a few servings daily is sufficient for general metabolic support and satiety.
10. What makes MCT oil essential on a keto diet?
On a MCT oil ketogenic diet, MCT oil accelerates ketone production, reduces sugar cravings, and provides stable energy. It helps users transition into ketosis more quickly and supports energy levels without relying on carbs. This makes it easier to maintain low-carb compliance, reduce hunger, and improve mental sharpness. MCT oil is especially helpful during the adaptation phase or when intermittent fasting, as it mitigates the fatigue and fog often experienced in early keto stages.

Conclusion
Medium-chain triglycerides have proven themselves as more than a wellness trend—they are a metabolically active, brain-enhancing, fat-burning class of fats that belong at the center of any modern nutritional strategy. Whether sourced from MCT-rich foods or delivered through high-quality oil, these powerful lipids provide a unique combination of fuel, focus, and flexibility. From managing weight and suppressing appetite to supporting cognitive clarity and hormonal balance, the benefits of MCT oil and the wider class of foods with MCTs extend across nearly every domain of health optimization.
Understanding how to use MCT oil, how much MCT oil per day is appropriate, and what foods are highest in MCTs gives individuals the tools they need to build a smarter, more energized diet. Whether you’re seeking sustained ketosis, better focus for ADHD, or a clean fuel source to power through your morning coffee, integrating these foods into your lifestyle can yield transformative results. The real superpower of MCTs lies in their versatility: they empower the body and mind without the energy rollercoaster of high-carb approaches.
So the next time you’re planning your meals or stocking your pantry, refer to this guide as your go-to MCT foods list—and let these high-performance fats work for your body, your brain, and your long-term goals.
Was this article helpful? Don’t let it stop with you. Share it right now with someone who needs to see it—whether it’s a friend, a colleague, or your whole network. And if staying ahead on this topic matters to you, subscribe to this publication for the most up-to-date information. You’ll get the latest insights delivered straight to you—no searching, no missing out.
Further Reading:
Is MCT Oil Good for Constipation? Exploring How It Affects Digestion and Gut Health
Best MCT Oil C8 C10 Guide: Benefits, Science, and Comparison Explained
MCT Oil Before Bed Weight Loss: Does Taking It at Night Really Work?



